Gain control & insight into ESG data
Introducing the NextWave and Alteryx solution that optimises your CSRD reporting, delivers compliance and enables detailed ESG analytics

The CSRD mandates have landed...
Navigating the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) legislation isn't an easy task. To deliver goals for increased economic flow to sustainable business models, the EU is demanding improved transparency to evaluate companies’ sustainability performance and related impacts and risks. The disclosures, based on the ‘double materiality’ concepts, require businesses (including EU subsidiaries of non-EU companies) to report on the ESG impact of their business activities, and the business impact of their ESG initiatives.
The CSRD applies to all companies that meet 2 of the 3 thresholds:
- €50 million in net turnover
- €25 million in assets
- 250 employees
-1.png?width=421&height=100&name=Boxed%20csrd%20(1)-1.png)
The CSRD is applicable to around 10,000 non-EU based organisations above a threshold for turnover (€150 million) generated in the EU, with an EU branch or subsidiary.
Starting in the financial year 2024 and reporting in 2025, public organisations already mandated to comply with the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) now have to comply with the CSRD, with a phased implementation approach for public and large private companies to follow. In addition to CSRD disclosures being publicly available, the legislation mandates third-party auditing of all disclosures for accuracy and completeness.
...and the data requirements are complex
Navigating the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) legislation isn't an easy task. To deliver goals for increased economic flow to sustainable business models, the EU is demanding improved transparency to evaluate companies’ sustainability performance and related impacts and risks. The disclosures, based on the ‘double materiality’ concepts, require businesses (including EU subsidiaries of non-EU companies) to report on the ESG impact of their business activities, and the business impact of their ESG initiatives.
Starting in the financial year 2024 and reporting in 2025, public organisations already mandated to comply with the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) now have to comply with the CSRD, with a phased implementation approach for public and large private companies to follow. In addition to CSRD disclosures being publicly available, the legislation mandates third-party auditing of all disclosures for accuracy and completeness.
Sanctions for non compliance
Coupled with the risk of reputational and brand damage, companies should pay close attention to the sanctions for non-compliance. These could include public statements indicating the personas involved, the issuance of a cessation order related to the area of infringement, and financial sanctions proportional to the profits and financial strength of the company.
Several hurdles are limiting progress on the CSRD
Many organisations are facing challenges in effectively operationalising their ESG data strategy. These include:
Continued reliance on MS Excel and manual End User Computing solutions to manage complex, heterogeneous, and disparate datasets
We see an over dependence on manual data sourcing, collection and data being stored in large Excel spreadsheets. Excel is not suitable to handle a large number of complex datasets that are coming from many different sources (departments, value chain partners), with data that comes in different formats.
Additionally, Excel sheets are more prone to crashing (resulting in data loss), prevent collaboration and team work (as there is a single file) and do not facilitate cross locational working.
Limitations in existing ESG reporting platforms
There is a lack of flexibility in pre-packaged ESG reporting platforms and modules to deliver high volume and intricate data transformations. Using these platforms and models often means that the data must be flexible, rather than the solution - resulting in a task that is very time-consuming and costly, especially when it has to be repeated multiple times to report on many different quantitative metrics.
These platforms, running to catch up with the large number of quantitative CSRD requirements, tend to be inflexible, and often rely on an extensive (3 month+) deployment cycle and need to be (re-) integrated and tested with existing platforms every time a new release is made. This problem will only increase as the CSRD requirements expand over time.
Gaps in ESG data
The CSRD requires companies to report on missing or inadequate data when reporting on their sustainability value chain. The lack of completeness of ESG data is a significant problem.
As data is held in disparate spreadsheets, there is a complete lack of transparency as to where there are data gaps, how big those gaps are and on what the impact is on downstream activities, such as risk modelling, portfolio management and overall ESG strategy. These data gaps will increase in importance as the CSRD is implemented, and we expect regulators will soon start to consider (capital) penalties for proxied data (in the case of Financial Institutions) and fines for Corporations. There is also a serious reputational and audit risk for missing or proxied data that can impact a company or financial institution. It is vital organisations have complete insight into their ESG data.
Lack of transparency
Organisations struggle with limitation in demonstrating reporting compliance. They experience difficulties in ensuring transparency of data from source to report.
Working with a spreadsheet or Sharepoint based solution, means that data is locked away and needs further resources to extract it and produce regular manually management reports. This whole ''industry'' is costly, inefficient, prone to error and time-consuming. It tends to consume the oxygen in the room, as teams are focused on extracting and manipulating data, with management requesting regular updates, that tend to lag what it really going on.
Limited analytics
An inability to focus on analytical insights means that there is a challenge when re-directing business actions to improve on ESG KPI’s. A lack of insight into the data makes it hard for management to make informed decisions, on strategy and portfolio management. Insights tends to be delayed, manually created and only presenting a partial picture (e.g. the lack of a complete data set and the impact on what is being presented may not be fully transparent).
41% of respondents cite constantly evolving and new ESG data as their top data management challenge
Bloomberg
88% of respondents said they don’t feel ready to meet the expectations of the CSRD. Only 7% say consider their reporting systems to be ready
Baker Tilly
Nearly half of companies still using spreadsheets to manage ESG data
ESG Today
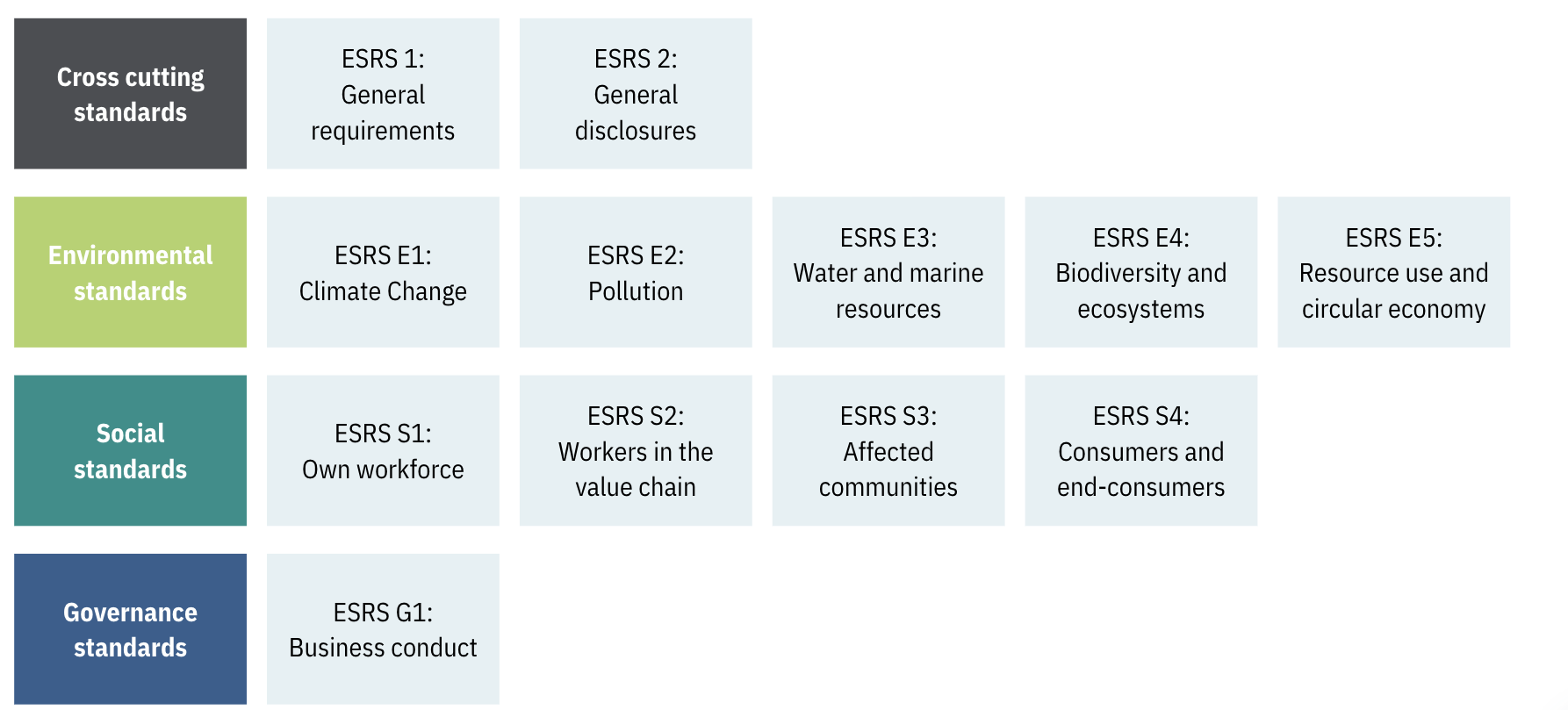
The CSRD-ESG Reporting Solution
The Solution
Pre-packaged Alteryx workflow accelerators, configurable to your CSRD data sources
Allowing you to:
- Connect directly to a multitude of systems, applications and files.
- Ingest high volume and granular data to complete data validations and cleansing.
- Manage data quality and transform the data for reporting and analysis purposes.
‘Plug-and-play’ CSRD reporting Alteryx macros – our off-the-shelf solution
- Pre-defined reporting coordinates that map quantitative data inputs to the CSRD disclosures and sub-forms.
- Assurance on meeting CSRD compliance requirements.
- Documentation that supports third-party risk assessment with transparency on data. lineage and transformations.
Automated reporting and analysis of ESG
data
This enables:
- Generation of reporting datasets ready to publish to relevant CSRD disclosures.
- Management reporting with driver-based analysis to explain movements in positions against ESG targets.
- Correlation analysis to help identify opportunities that optimise performance considering ESG factors.
The Benefits
Reduced cost of change and operating cost

Faster speed
to market

Improved data
literacy

Reduced audit
risk and cost

Improved resilience
and reporting flexibility

Improved compliance assurance
The implementation of the CSRD-ESG Reporting Solution:
a 4 stage process
Stage A: Data sourcing & import
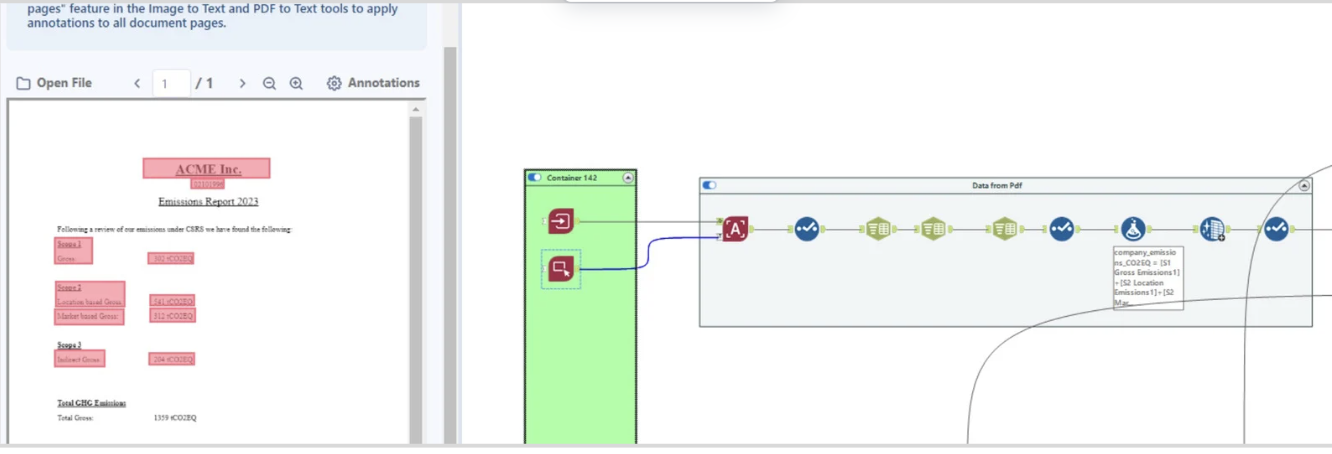
ESG data is sourced from a wide variety of places (departments, value chain partners, 3rd party vendors), and comes in various formats (both structured and unstructured).
- Data imports are created on a per-client basis, dependent on company data structure. Data is sourced in a dynamic and adaptable manner in varying formats, including:
- SQL databases
- Spreadsheets
- Emails
- PDFs
- Bespoke data connectors have been created for each source of the truth, and these connections are built into the main Alteryx workflow.
Stage B: Data normalisation and preparation
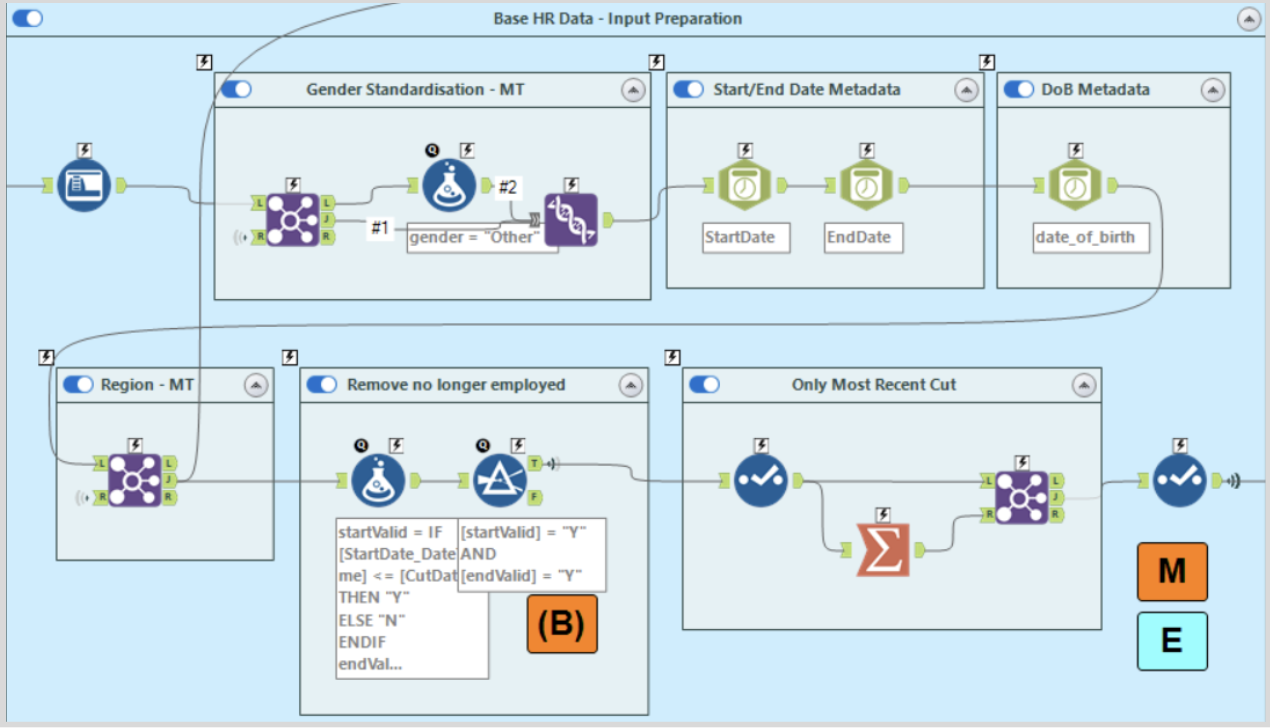
Once data has been sourced and ingested into the workflow, it must be cleansed and normalised in preparation for parsing. A variety of data preparation methods can be harnessed, including:
- Data cleansing to ensure quality and completeness.
- Setting of metadata (data types) of each field.
- Bespoke mapping tables, used to standardise data.
- Preparatory calculations.
- Filtering of unnecessary data, to ensure runtimes are kept to a minimum and required processing power isn't excessive.
- All data cleansing and preparation methods implemented are bespoke and built on a per-client basis, dependent on the requirements of the incoming sourced data.
Stage C: Data processing
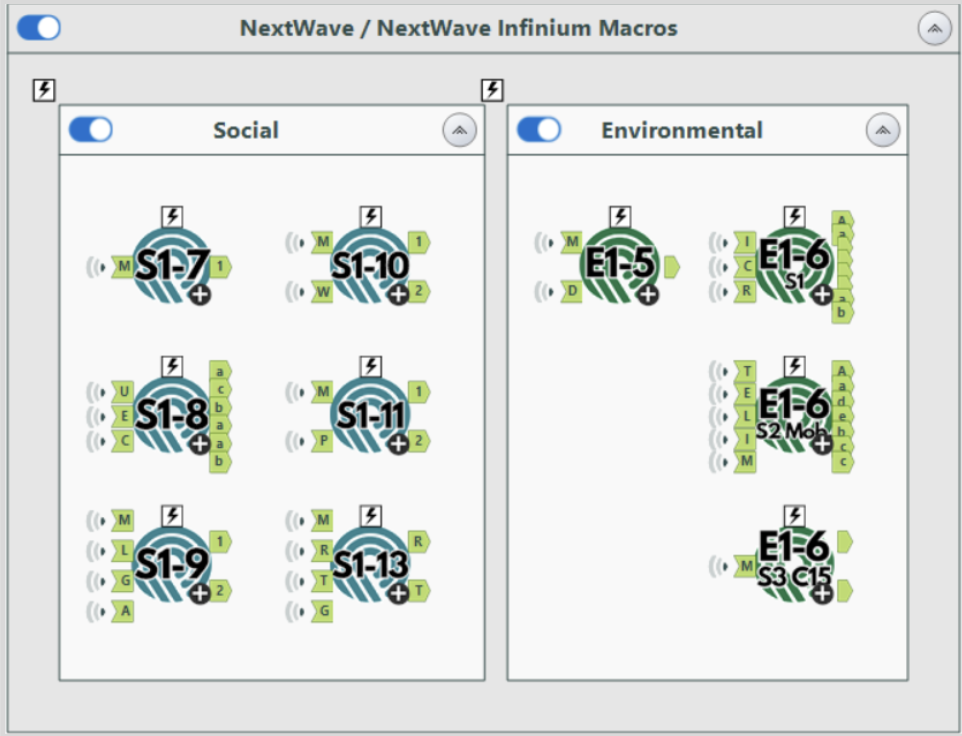
After preparation, all relevant CSRD pre-built Alteryx Macros, representing the quantitative reporting requirements relevant to the client's business needs and reporting needs, are placed into the workflow. The Alteryx workspace allows organisations to select and acquire the CSRD Alteryx Macros they need.
- Prepared data is fed in, and relevant required data fields are selected in the custom macro interfaces.
- Inbuilt workflows then process the data as constructed and create outputs for both CSRD regulatory reporting purposes as well as internal trends analysis (Stage D).
Stage D: Reporting outputs & analytics
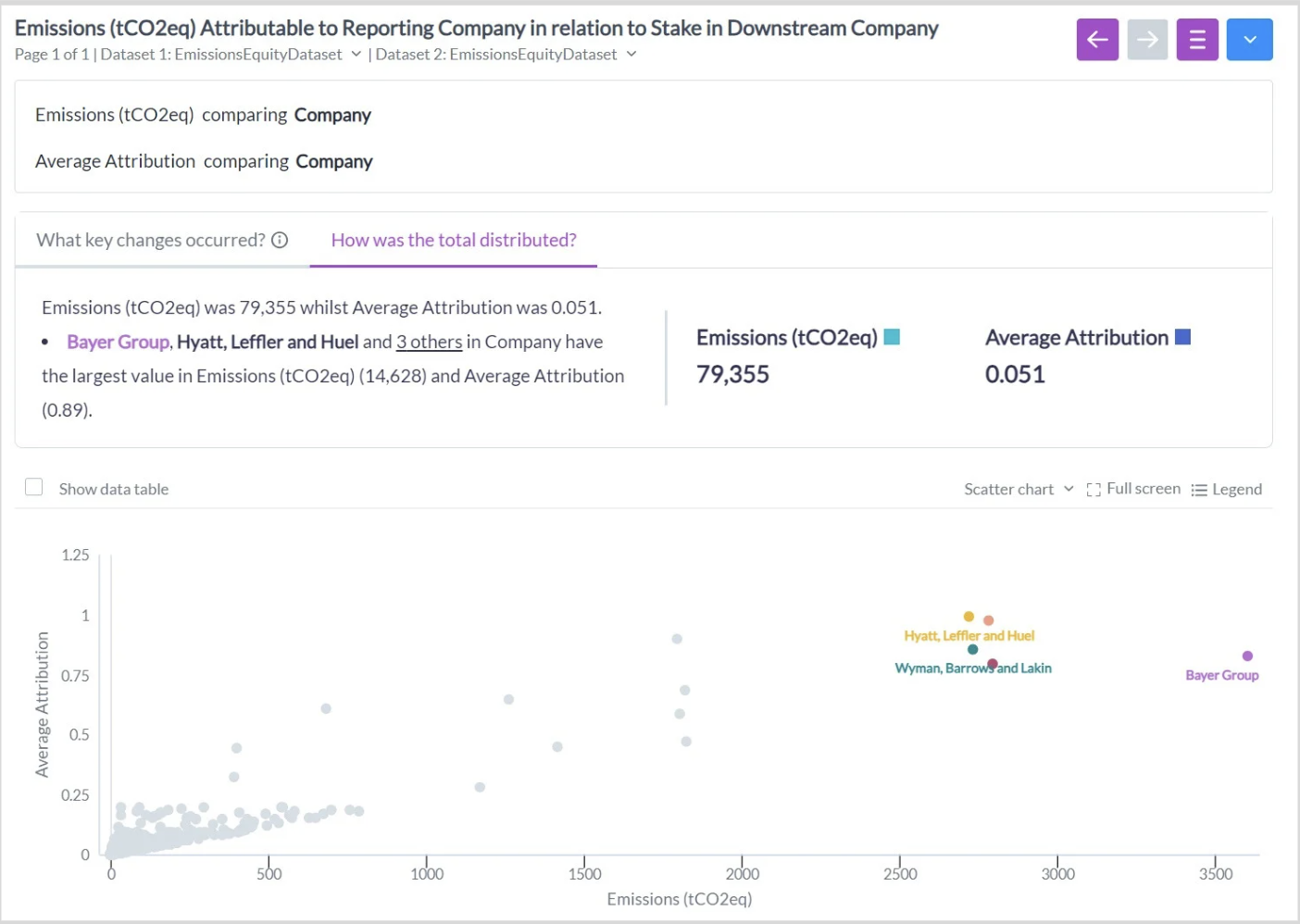
The Alteryx Macro outputs can be constructed directly as tables for static regulatory CSRD reporting, or can be integrated with existing monitoring and reporting platforms. Additionally, Alteryx Auto Insights provides visual, interective reports for a more detailed overview of results. Alteryx Auto Insights leverages AI for a more detailed trends analysis tracking of key metrics, essential for making strategic decisions and driving overall strategy.
Additional CSRD Related Services:
Complementary to the Alteryx CSRD-ESG Reporting Solution, NextWave offers a variety of additional technology solutions and consultancy services to assist corporates and financial institutions with their sustainability reporting, analytics, and strategy.
ESG project and program management
Double materiality
assessments
Business and data
requirements and collection
The definition of the business and data requirements needed to support CSRD reporting. Data collection supported with AI.
Supply chain analytics
and entity resolution
CSRD - ESG Reporting Alteryx Solution
ESG strategy
and advisory
Leveraging insights from trend analytics, receive strategic recommendations for ESG improvement.
Our experts
Our team have decades of experience in top-tier global banks and have a proven track record of delivering successful strategy plans and executing business solutions for clients. We are committed to driving forward sustainable finance practices in the industry. We work with our clients and technology partners to create positive social and environmental impact, while also generating long-term financial value.
About the NextWave and Alteryx partnership
The NextWave and Alteryx partnership brings together business expertise and leading analytics solutions to automate your ESG data and reporting processes. Our longstanding partnership combines deep industry experience, complex data engineering capabilities and analytical skills with the power of Alteryx. When tackling the challenges of dealing with ESG data management and the CSRD regulation, we offer a variety of services, ranging from ESG strategy, regulatory advisory, program planning, materiality assessments, and data collection, as well as data optimisation and reporting via our CSRD-ESG Regulatory Reporting Solution.
Interested in digital acceleration?
Subscribe to NextWave for occasional email updates on the latest technology, acceleration approaches, news and NextWave events. You can unsubscribe from these communications at any time.




